Continuing to Work on Her Dissertation
The significance of dissertation writing in the world of academia is unparalleled. A good dissertation paper needs months of research work and marks the end of your academic journey.
If one showcases the ability to conduct independent research in their preferred area of study and presents results that fill an evident research gap in the existing literature, the work will improve employability (among other things).
Although the dissertation writing process is demanding, there is no need to bow your head to this project's pressure and the surrounding scaremongering.
This comprehensive step-by-step guide on how to write a dissertation will serve as a tool to help you with the task at hand, whether you are an undergraduate, Masters or PhD student working on your dissertation project or a Masters' student developing a thesis for a professional qualification.
What is a Dissertation – Definition
Before we list the stages of writing a dissertation, it will make sense to look at the definition of a dissertation.
The Cambridge dictionary states that a dissertation is a long piece of writing on a particular subject; especially on that is done to receive a degree at college or university, but that is just the tip of the iceberg because a dissertation project has a lot more meaning and context.
To understand a dissertation's definition, one must have a methodological understanding of an essay or a thesis. A dissertation is like an essay that includes research and information at a much deeper level.
Almost all undergraduate, postgraduate and doctorate students in the UK are required to successfully deliver a final dissertation project and provide value to the academic community as part of their degree programs.
Difference between Dissertation and Thesis
Both the terms dissertation and thesis are used interchangeably across the world (and may vary between universities and regions), but the key difference between them is when they are completed.
The thesis is a project that marks the end of a degree program, whereas the dissertation project can occur during the degree. Hanno Krieger (Researchgate, 2014) explained the difference between dissertation and thesis as follows:
"Thesis is the written form of research work to claim an academic degree, like PhD thesis, postgraduate thesis, and undergraduate thesis. On the other hand, a dissertation is only another expression for the written research work, similar to an essay. So the thesis is the more general expression."
In the end, it does not matter whether it is a bachelors', master or PhD dissertation one is working on because the structure and the steps of conducting research are pretty much identical. Although, doctoral-level dissertation papers are much more complicated and detailed.
Problems Students Face When Writing a Dissertation
Expect to come across some troubles and turbulences if you don't yet know the steps of how to write a dissertation. Even the smartest students are bent out of shape by this menacing project if they don't wrap their heads around the required approach.
A dissertation project is unlike any essay paper you have ever committed to because of the details of planning, research and writing it involves. One can expect rewarding results at the end of the process if the correct guidelines are followed. Still, as indicated previously, there will be multiple challenges to deal with before reaching that milestone.
The following are the two most significant problems students face when working on the dissertation project.
1. Poor Project Planning
Delaying to start working on the dissertation project is perhaps the most common problem. Students think they have sufficient time to complete the paper, delaying the start to the point where they start to stress out about the looming deadline.
Here is a solution to all your dissertation project planning problems.
2. Inadequate Research Skills
The writing process becomes a mountain of problems if one does not have the required academic research experience. Professional dissertation writing goes well beyond collecting a few relevant reference resources.
Depending on the dissertation's topic and the academic qualification you are a candidate for, you may be required to base your dissertation paper on primary research.
This will mean that in addition to secondary data, you will also need to collect data from the specified participants and test the hypothesis. The practice of primary collection is time-consuming since all the data must be analysed in detail before results can be withdrawn.
3. Failure to Meet the Strict Academic Writing Standards
Research is serious business everywhere. Failure to follow the language, style, structure, and formatting guidelines as provided by your department and/or institution when writing the dissertation paper can make matters worse. It is recommended to read the dissertation handbook before starting the write-up thoroughly.
 At Research Prospect, our expert writers can help you with your quantitative dissertation whether you are a student of sports science, medical or biological science, education or business, psychology, social sciences, engineering, project management, or any other science-based degree. We guarantee 100% commitment, 100% Plagiarism-free work, 100% Confidentiality and 100% Satisfaction.
At Research Prospect, our expert writers can help you with your quantitative dissertation whether you are a student of sports science, medical or biological science, education or business, psychology, social sciences, engineering, project management, or any other science-based degree. We guarantee 100% commitment, 100% Plagiarism-free work, 100% Confidentiality and 100% Satisfaction.
Does your Dissertation Have the Following?
- Great Research/Sources
- Perfect Language
- Accurate Sources
If not, we can help. Our panel of experts makes sure to keep the 3 pillars of the Dissertation strong.

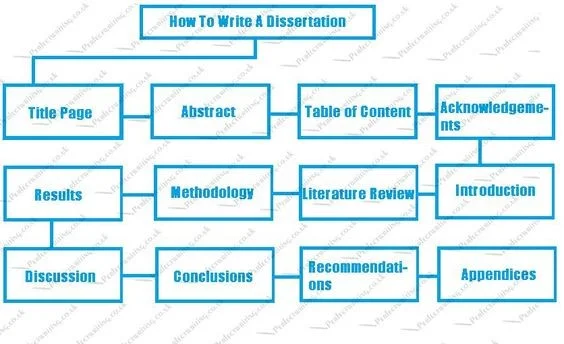
Steps of How to Write a Dissertation
For those stressing out about developing an extensive paper capable of filling a gap in research whilst adding value to the existing academic literature—conducting exhaustive research and analysis—and professionally using the knowledge gained throughout their degree program, there is still good news in all the chaos.
We have put together a guide that will show you how to start your dissertation and complete it carefully from one stage to the next.
Step #1: Find an interesting and manageable research topic.
A clearly defined topic is a prerequisite of any successful independent research project. An engaging yet manageable research topic can produce an original piece of research work that results in a higher academic score.
Unlike essays and assignments, when working on their thesis or dissertation project, students get to choose their topic of research.
And so, if all pieces of the puzzles are put together in a holistic and multidisciplinary fashion, a dissertation or thesis can also be the most rewarding task you have ever committed to.
Your chosen research topic should be neither too broad nor too narrow, allowing you to collect the required secondary and primary data in a relatively short time.
Focusing on an issue that ignites your interest in a particular academic theory and stirs your excitement levels is likely to produce a unique piece of work. Our dissertation topics library has thousands of free research topics in all academic subjects.
Alternatively, you can consider reading newspapers, academic journals, articles, course materials, and other media to identify relevant issues to your area of study and find some inspiration to get going.
We recommend students work closely with their supervisor to agree to a narrowed but clear research plan.
Here is what Michelle Schneider, learning adviser at the University of Leeds, had to say about picking the research topics, "Picking something you're genuinely interested in will keep you motivated. Consider why it's important to tackle the topic you have chosen", she added.
More on how to choose a great dissertation topic
Step #2: Develop a first-class dissertation proposal.
Once the research topic has been selected, you can proceed to develop a solid dissertation proposal. The proposal paper allows you to convince your supervisor or the committee members (for masters and PhD programs) on the significance of your research proposal.
Through the research proposal, you will be expected to prove that your work will significantly value the academic and scientific communities by addressing complex and provocative questions.
Proposal papers are much shorter in length but follow a similar structure as an extensive dissertation paper. If the proposal is not mandatory in your university, you should still create one outline of the key points that the actual dissertation paper will cover.
Typical contents of the dissertation paper are as following;
- A brief rationale for the problem your dissertation paper will investigate.
- The hypothesis or hypothesis you will be testing.
- Research objectives you wish to address.
- How you would be contributing to the knowledge of the scientific and academic community.
- How you will be going to find answers to the key research question(s).
- What research approach you will adopt.
- The kind of population of interest you would like to generalise your result(s) to (especially in the case of quantitative research).
- What sampling technique(s) you would employ and why that and not other sampling techniques.
- What ethical considerations have you taken to gather data.
- Who the stakeholders in your research are/might be.
- The future implications and limitations you see your research establishing.
How to Structure the Dissertation Proposal
Do not overcomplicate the format of your proposal. Keeping it simple keeps your readers will remain engaged. The following are the fundamental focal points that must be included:
- Title of your dissertation: Academic research titles should not be more than 12 words in length, ideally. The topic should be clearly identifiable from your research title.
- Research aim: The study's overall purpose should be clearly stated in terms of the broad statements of the desired outcomes. Try and paint the picture of your research, emphasising what you wish to achieve as a researcher.
- Research objectives: The key research questions you wish to address as part of the project should be listed. Narrow down the focus of your research and aim for not more than four objectives. Your research objectives should be linked with the aim of the study or a hypothesis.
- Literature review: Consult with your supervisor to check if you are required to use any specific academic sources as part of the literature review process. If that is not the case, find out the most relevant theories, journals, books, schools of thought, and publications that will be used to construct arguments in your literature research.
Remember that literature research is all about giving credit for other authors' works on a similar topic.
- Research methods and techniques: Depending on your research topic, you might be required to conduct empirical research to satisfy the study's objectives. Empirical research uses primary data such as questionnaires, interview data, and surveys to collect.
On the other hand, if your dissertation is based on secondary (non-empirical) data, you can stick to the existing literature in your area of study. Clearly state the merits of your chosen methods of research under the methodology section.
- Expected results: As you explore the research topic and analyse the data in the previously published papers, you will begin to build your expectations around the study's potential outcomes. List those expectations here.
- Project timeline: Let the readers know exactly how you plan to complete all the dissertation project parts within the timeframe allowed. You might want to learn more about Microsoft Project and Gantt Charts to create easy-to-follow and high-level project timelines and schedules.
- References: The list of academic sources used to gather information for the proposed paper will be listed under this section using the appropriate referencing style. Ask your supervisor which referencing style you are supposed to follow.
Check out our comprehensive guidelines on how to write a first-class dissertation proposal.
Step #3: Investigation, Research and Data Collection
This is perhaps the most critical stage of the dissertation writing process. One should not waste their time using outdated and irrelevant academic sources that are likely to put hard work in jeopardy.
Finding relevant and highly authentic reference resources is the key to succeeding in the dissertation project, so it is advised not to rush this process. Here are some of the things that should be considered when conducting research.
You cannot read everything related to your topic. Although the practice to read as much material during this stage is rewarding, it is also imperative to understand that it is impossible to read everything that concerns your research.
This is true especially for undergraduate and master's level dissertations that must be delivered within a specific timeframe. So, it is important to know when to stop! Making a timeline at this stage will help you stay organised without losing sight of the goal you want to achieve.
Once the previous research and the associated limitations are well understood, it is time to move on.
However, review at least the salient research and work done in your area. By salient, we mean research done by pioneers of your field. For instance, if your topic relates to linguistics and you haven't familiarised yourself with relevant research conducted by, say, Chomsky (the father of linguistics itself), your readers may find your 'lack of knowledge' disconcerting.
So, to come off as truly knowledgeable in your own field at least, don't forget to read salient works in the field/topic!
Different research strategies you can use in a dissertation paper
- Use an authentic research database to find reference resources.
Most students start the reference material finding process with desk-based research. However, this research method has its own limitation because it is a well-known fact that the internet is full of bogus information and fake information spreads fasters on the internet than truth does.
So, it is vitally important to pick your reference material from reliable resources such as Google Scholar and Researchgate. Ibibio and Bartleby. Wikipedia is not considered a reliable academic source in the academic world, so it is recommended to avoid citing Wikipedia content.
Never underrate the importance of the actual library. The supporting staff at a university library can be of great help when it comes to finding interesting and reliable publications.
- Record as you learn
All information and impressions should be recorded as notes using online tools such as Evernote to avoid confusion later. You do not want to lose an important piece of information you had planned to present as an argument in the dissertation paper.
Looking for quantitative dissertation help?
Research Prospect to the rescue then!
We have expert writers on our team who are skilled at helping students with quantitative dissertations across a variety of STEM disciplines. Guaranteeing 100% satisfaction!

Step #4: Write a flawless dissertation.
Start to write a fantastic dissertation immediately once the supervisor or the graduate committee has accepted the proposal and all the necessary desk-based research has been conducted.
Remember: This basket will put all your eggs in to develop one mind-blowing yet fact-based product. Most students panic when they realise the number of hours they need to create a well-versed dissertation paper, even if they found the writing process's previous steps inspiring.
Dissertation Outline
Ever heard of the quote, "If you fail to plan, you are planning to fail"? Try not to fall prey to it. The whole process will become that much more manageable if you have a basic dissertation outline or plan. Do not mix a dissertation outline with the proposal.
A dissertation outline serves an entirely different purpose as it provides a framework of your action plan and how it will be implemented.
How to Write a Dissertation Introduction Chapter
The introduction chapter of the dissertation paper provides the background, problem statement and research questions. Here, you will inform the readers why it was important for this research to be conducted and which key research question(s) you expect to answer at the end of the study.
Definitions of all the terms and phrases in the project are provided in this first chapter of the dissertation paper. The research aim and objectives generally remain unchanged from the proposal paper and are expected to be listed under this section.
Click here to check our comprehensive guidelines on how to write the introduction of a dissertation.
How to Write a Dissertation Literature Review Chapter
This chapter allows you to demonstrate to your readers that you have done sufficient research around the chosen topic and understand previous similar studies' findings. Any research limitations that your research incorporates are expected to be discussed in this section.
And make sure to summarise the viewpoints and findings of other researchers in the dissertation literature review chapter. Show to the readers that there is a research gap in the existing work and your job is relevant to it to justify your research value.
 Many students get carried away when working on the literature review chapter. It is important to remember that you have a specific word count limit for the full dissertation paper to work with. Make sure that you are devoting enough words to each chapter of the paper. If you have been provided grading criteria by your university, it's better to use it to work out the word count's nominal split.
Many students get carried away when working on the literature review chapter. It is important to remember that you have a specific word count limit for the full dissertation paper to work with. Make sure that you are devoting enough words to each chapter of the paper. If you have been provided grading criteria by your university, it's better to use it to work out the word count's nominal split.
Learn more about how to write a literature review of the dissertation.
Also read: How to Write a Dissertation in 10 Days or Less
How to Write Dissertation Methodology
The methodology chapter of the dissertation provides an insight into the methods employed to collect data from various resources and flows naturally from the literature review chapter.
In simple words, you will be expected to explain what you did and how you did it; helping the readers understand that your research is valid and reliable. When writing the methodology chapter for the dissertation, make sure to emphasise the following points:
- The type of research performed by the researcher
- Methods employed to gather and filter information
- Techniques that were chosen for analysis
- Materials, tools and resources used to conduct research (typically for empirical research dissertations)
- Limitations of your chosen methods
- Reliability and validity of your measuring tools and instruments (e.g. a survey questionnaire) are also typically mentioned within the mythology section. In case you used a pre-existing data collection tool, cite its reliability/validity estimates here, too.
 Make use of the past tense when writing the methodology chapter.
Make use of the past tense when writing the methodology chapter.
How to Write Dissertation Findings
The key results of your research are presented in the dissertation findings chapter. Many academics consider this chapter to be the icing on the cake stage of the dissertation writing process. It gives authors the ability to validate their own intellectual and analytical skills.
How to Write a Dissertation Conclusion
Cap off your dissertation paper with a summary of the study and a brief report of the findings. In the concluding chapter, you will be expected to demonstrate how your research will provide value to other academics in your area of study and its implications.
It is recommended to include a short 'recommendations' section that will elaborate on the purpose and need for future research to elucidate the topic further.
Here is a detailed article on how to write a dissertation conclusion
References
Follow the referencing style following the requirements of your academic degree or field of study. Make sure to list every academic source used with a proper in-text citation. It is important to give credit to other authors' ideas and concepts.
Note: Keep in mind whether you are creating a reference list or a bibliography. The former includes information about all the various sources you referred to, read from or took inspiration from for your own study. However, the latter includes things you used as well as those you only read but didn't end up citing in your own dissertation.
Completing the First Draft
Stay focused, avoid distractions, stick to the plan and follow the outline to complete the first dissertation draft. The most important thing is to keep your head down and continue writing as much as possible daily until all paper chapters are completed.
Have a firm belief in your writing skills. You have what it takes to produce an excellent dissertation paper.
Step #5: Proofread, edit and improve – Don't risk months of hard work.
Experts recommend that you should complete the total dissertation before starting to proofread and edit your work. You need to refresh your focus and reboot your creative brain before getting back to another critical stage of the process.
If possible, leave space of at least a few days between the writing and the editing steps so when you get back to the desk, you can recognise your grammar, spelling and factual errors.
It is crucial not to underestimate this period to ensure the final work is polished, coherent, well-structured and free of any structural or factual flaws. Daniel Higginbotham from Prospects UK states that:
"Leave yourself sufficient time to engage with your writing at several levels – from reassessing the logic of the whole piece to proofreading to checking you've paid attention to aspects such as the correct spelling of names and theories and the required referencing format."
Editing and Proofreading Your Dissertation Paper
What is the difference between editing and proofreading? Editing means that you are focusing on the essence of your dissertation paper. In contrast, proofreading is the process of reviewing the final draft piece to ensure accuracy and consistency in formatting, spelling, facts, punctuation, and grammar.
Editing: Prepare your work for submission by condensing, correcting and modifying (where necessary). When reviewing the paper, make sure that there are coherence and consistency between the arguments you presented.
If an information gap has been identified, fill that with an appropriate piece of information gathered during the research process. It is easy to lose sight of the original purpose if you become over-involved when writing.
Cut out the unwanted text and refine so your paper's content is to the point and concise.
Proofreading: Start to proofreading your paper to identify formatting, structural, grammar, punctuation and referencing flaws. Read every single sentence of the paper no matter how tired you are because few puerile mistakes can compromise your months of hard work.
Many students struggle with the editing and proofreading stages due to their lack of attention to details. Consult a skilled dissertation editor if you are unable to find your flaws. You may want to invest in a professional dissertation editing and proofreading service to improve the piece's quality to First Class.
Some Tips on How to Write a Dissertation
Communication with Supervisor – Get Feedback
Make sure to regularly communicate with your supervisor to produce a first-class dissertation paper. If possible, request them to comprehensively review the contents of your dissertation paper before final submission.
Their constructive criticism and feedback concerning different study areas will help you improve your piece's overall quality. Keep your supervisor updated about your research progress and discuss any problems that you come up against.
Meeting them on a weekly or monthly basis will help you to ensure regular communication. You may end up receiving a low grade on your dissertation if this important step is not taken seriously. Getting feedback on your work will help you gain valuable marks and simplify the process of revising your dissertation.
Organising Your Time
A dissertation is a lengthy project spanning over a period of months to years, and therefore it is important to avoid procrastination. Stay focused, and manage your time efficiently. Here are some time management tips to help you make the most of your time as you research and write.
- Don't be discouraged by the inherently slow nature of dissertation work, particularly in the initial stages.
- Set clear goals and work out your research and write up a plan accordingly.
- Allow sufficient time to incorporate feedback from your supervisor.
- Leave enough time for editing, improvement and proofreading and formatting the paper according to your school's guidelines. This is where you break or make your grade.
- Work a certain number of hours on your paper daily.
- Create a worksheet for your week.
- Work on your dissertation for time periods as brief as 45 minutes or less.
- Stick to the strategic dissertation timeline, so you don't have to do the catchup work.
- Meet your goals by prioritizing your dissertation work.
- Strike a balance between being overly organised and not organised enough.
- Limit activities other than dissertation writing and your most necessary obligations.
- Keep 'tangent' and 'for the book' files.
- Create lists to help you manage your tasks.
- Have 'filler' tasks to do when you feel burned out or in need of intellectual rest.
- Keep a dissertation journal.
- Pretend that you are working in a more structured work world.
- Limit your usage of email and personal electronic devices.
- Utilise and build on your past work when you write your dissertation.
- Break large tasks into small manageable ones.
- Seek advice from others, and do not be afraid to ask for help.
Dissertation examples
Here are some samples of a dissertation to inspire you to write mind-blowing dissertations and to help bring all the above-mentioned guidelines home.
DE MONTFORT University Leicester – Examples of recent dissertations
Dissertation Research in Education: Dissertations (Examples)
However, this method has one prominent limitation: combining qualitative and quantitative research can be difficult because they both are different in terms of design and approach.
In many ways, they are contrasting styles of research and so, care must be exercised when basing your dissertation on mixed methods of research.
When choosing the research method for your own dissertation, it would make sense to carefully think about your research topic, research questions and research objectives to make an intelligent decision in terms of the philosophy of research design.
Dissertations based on mixed methods of research can be the hardest to tackle even for PhD students. Our writers have years of experience in writing flawless and to the point mixed methods-based dissertations to be confident that the dissertation they write for you will be according to the technical requirements and the formatting guidelines. Read our guarantees to learn more about how you can improve your grades with our dissertation services.
Check our dissertation samples here.
How long is a Dissertation?
The entiredissertation writing process is complicated and spans over a period of months to years, depending on whether you are an undergraduate, master's, or PhD candidate. Marcus Beck, a PhD candidate, conducted fundamental research a few years ago, research that didn't have much to do with his research but returned answers to some niggling questions every student has about the average length of a dissertation.
A software program specifically designed for this purpose helped Beck to access the university's electronic database to uncover facts on dissertation length.

The above illustration shows how the results of his small study were a little unsurprising. Social sciences and humanities disciplines such as anthropology, politics, and literature had the longest dissertations, with some PhD dissertations comprising 150,000 words or more.
Engineering and scientific disciplines, on the other hand, were considerably shorter. PhD level dissertations generally don't have a predefined length as they will vary with your research topic. Ask your school about this requirement if you are unsure about it from the start.
 Focus more on the quality of content rather than the number of pages.
Focus more on the quality of content rather than the number of pages.
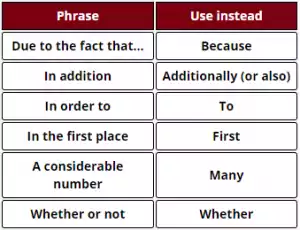
Style of a Dissertation
Phrases to Avoid
No matter the style or the structure you are following, it is best to keep your language simple. Avoid the use of buzzwords and jargon.
A Word on Stealing Content (Plagiarism)
Very straightforward advice to all students, DO NOT PLAGIARISE.
Plagiarism is a serious offence. You will be penalised heavily if you are caught plagiarising. Don't risk years of your hard work as many students in the past have lost their degrees for plagiarising. Here are some tips to help you make sure you don't get caught.
- Copying and pasting from an academic source is an unforgivable sin. Rephrasing text retrieved from another source also falls under plagiarism; it's called paraphrasing. Summarising another's idea(s) word-to-word, paraphrasing and copy-pasting are the 3 main forms plagiarism can take.
- If you must directly copy full sentences from another source because they fill the bill, always enclose them inside quotation marks and acknowledge the writer's work with in-text citations.
Are you struggling to find inspiration to get going? Not sure where to begin? Is deadline getting closer? Don't be overwhelmed! Research Prospect dissertation writing services have helped thousands of students achieve desired outcomes. Click here to get help from writers holding either a masters or PhD degree from a reputed UK university.
Tips to Avoid Plagiarism in a Dissertation
FAQs About How to Write a Dissertation
You must choose any topic that ignites your interest, makes you excited to learn more about it and is doable. In sum, you must choose an interesting and manageable topic.
You cannot read everything related to your topic. Although the practice to read as much material during this stage is rewarding. But it is important to know when to stop! Making a timeline at this stage will help you stay organised without losing sight of the goal you want to achieve.
The introduction chapter of the dissertation paper provides the background, problem statement, and research questions. Here, you will inform the readers why it was important for this research to be conducted and which key research questions you expect to answer at the end of the study .
This chapter allows you to tell your readers that you have done sufficient research around the chosen topic and understand previous similar studies' findings. Any research limitations that your research incorporates are expected to be discussed in this section. You must summarise the viewpoints and findings of other researchers in the dissertation literature review chapter.
Make sure to include the following points in the methodology:
- The type of research performed by the research
- Methods employed to gather and filter information
- Techniques are chosen for analysis.
- Materials, tools, and resources used to conduct research (typically for empirical research dissertations)
- Limitations of your chosen methods
Source: https://www.researchprospect.com/how-to-write-a-dissertation-step-by-step-guide/
0 Response to "Continuing to Work on Her Dissertation"
Post a Comment